A short overview of the Anti-Atlas, Morocco
DR.Hervé Rezeau, DR.Cyril Chelle-Michou & DR.Michael Calder
SEG Student Chapter of Geneva (Switzerland)
SEG Student Chapter of Montpellier (France)
INTRODUCTION
Geology of Morocco has been subdivided into four structural domains, from north to south they are the following: the Rif domain, the Meseta domain, the High Atlas, and the Anti-Atlas, as they are shown in (Figure 1).
The Rif Range extends along the Mediterranean coast from the Kabylian-Tellian belts up to the Strait of Gibraltar. South of it, the Meseta domain is located, where elevated plateaus and intramontane basins occur. Further south the High Atlas system is found, which displays several massifs close to 4000 m, including the highest peak of northern Africa (Jebel Toubkal). The Middle Atlas represents a branch of the Atlas system that extends obliquely across the Meseta domain, and exceeds 3000 m in elevation. Finally, the Anti-Atlas domain is found, which rises forming a massive mountain that achieves up to 2700 m. Further south the elevation decreases both southward and westward from ca. 1000 m to less than 200 m close to the Atlantic.
Figure 1: Elevation map of Morocco and neighbouring countries from GTOPO30 database (A. Michard et al. 2008)
GEOLOGICAL SETTING OF THE ANTI-ATLAS
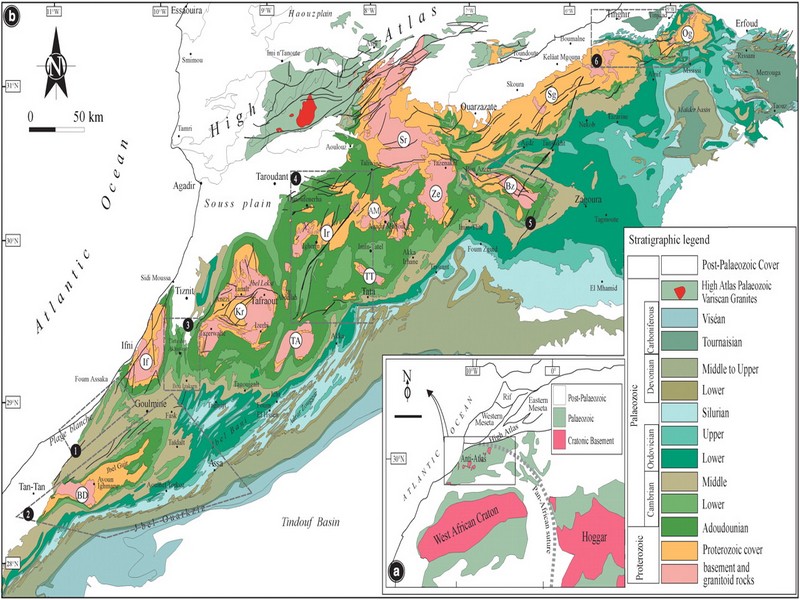
The Anti-Atlas mountain belt is located in the northern part of the West African Craton (WAC). It is stretching NE-SW and is characterized by Precambrian to late Proterozoic rocks covered by younger sediments of Edicaran to Cambrian in age. The geological boundary between the Anti-Atlas and High Atlas is structurally marked by the South Atlas fault (SAF) (Fig.2). The Anti-Atlas massif is a zone of wide domal uplift with much weaker Alpine age deformation. The volcanics and conglomerates rocks from the Ouarzazate & Bou Salda group in the North-East are surrounding the older volcanics rocks
The Anti-Atlas mountain belt is located in the northern part of the West African Craton (WAC). It is stretching NE-SW and is characterized by Precambrian to late Proterozoic rocks covered by younger sediments of Edicaran to Cambrian in age. The geological boundary between the Anti-Atlas and High Atlas is structurally marked by the South Atlas fault (SAF) (Fig.2). The Anti-Atlas massif is a zone of wide domal uplift with much weaker Alpine age deformation. The volcanics and conglomerates rocks from the Ouarzazate & Bou Salda group in the North-East are surrounding the older volcanics rocks and turbidite sequences from the Sahgro Group and the Pan-African granite intrusions. This geomorphological feature is commonly called inliers (“boutonnière” in French) and is the result of an exposed older rock formation surrounded by younger rock, and is due to a high erosion rate of rocks with different hardness but also encouraged by deformation such as folding and faulting (Gasquet et al. 2005). Several slivers of ophiolites are present in the Anti-Atlas belt, the best preserved are situated in the Bou Azzer, Siroua and Iriri region, which represent remnant of an ocean closure. The basement is composed of schists, granites and mylonites of Paleoproterozoic age. The latest Variscan and Alpine orogenic events overprint most of the Anti-Atlas geological province and thus complicate the Pre- Cambrian geodynamic interpretation. However, two main periods of tectono-thermal magmatic activity (Gasquet et al. 2005) are now recognised :
(i)A Palaeoproterozoic period, corresponding to the Eburnean (Birimian) orogeny,
(ii)A Neoproterozoic period, corresponding to the Pan-African orogeny.
Figure 2: Schematic map of the Anti-Atlas Precambrian inliers (Boutonnière), and location of the maps, satellite views and lithospheric profile presented hereafter (Gasquet et al. 2008)
Source web : DR.Hervé Rezeau, DR.Cyril Chelle-Michou & DR.Michael Calder unige.ch
Les articles en relation

Kasbahs et ksour du sud-est marocain: TAMGROUT (Géoparc jbel bani)
Kasbahs et ksour du sud-est marocain: TAMGROUT (Géoparc jbel bani) Ce ksar est situé à 25 Km de Zagora en direction de M'Hamid. Il est construit sur un plateau pratiquement désertique et comprend 200 h
Savoir plus...
ISS : le Soyouz a bien été victime d’un acte de sabotage
ISS : le Soyouz a bien été victime d’un acte de sabotage Le trou dans la carlingue du véhicule Soyouz, actuellement amarré à la Station spatiale internationale, a bien ét&eacu
Savoir plus...
Le Territoire Soutenable du Géoparc Jbel Bani (TSGJB) : Un modèle de tourisme durable au Maroc
Le Territoire Soutenable du Géoparc Jbel Bani (TSGJB) : Un modèle de tourisme durable au Maroc Le Geoparc Jbel Bani, situe au sud du Maroc, représente une initiative remarquable en matière de tou
Savoir plus...
Honor View 20, un smartphone avec un trou dans l'écran
Honor View 20, un smartphone avec un trou dans l'écran Trois innovations dans le nouveau smartphone haut de gamme Honor : un capteur caché directement dans l’écran, un capteur de 48 millions de pixels e
Savoir plus...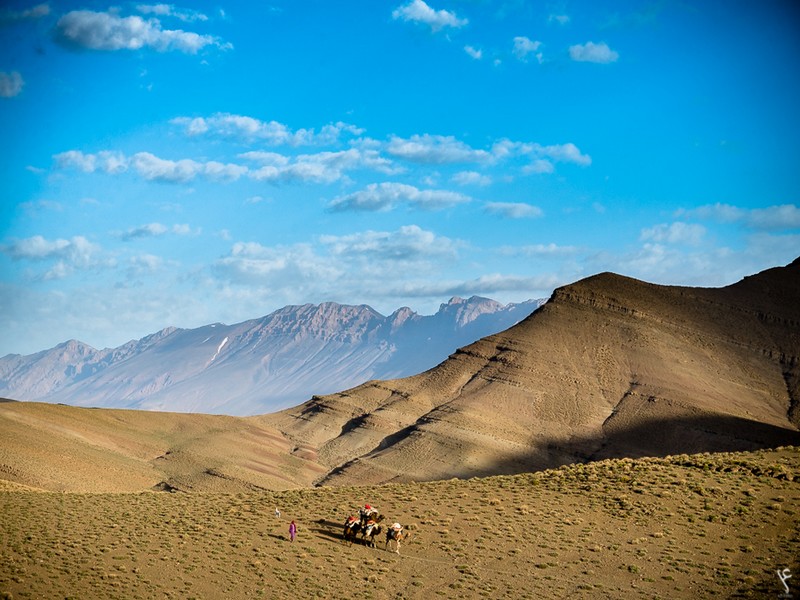
Sur la vague du nouveau Maroc
Sur la vague du nouveau Maroc Mettre le pied une deuxième fois sur le sol marocain répondait pour nous cinq à une soif de mieux connaître ce pays qui nous hante et nous attire avec ses mille couleurs, ses s
Savoir plus...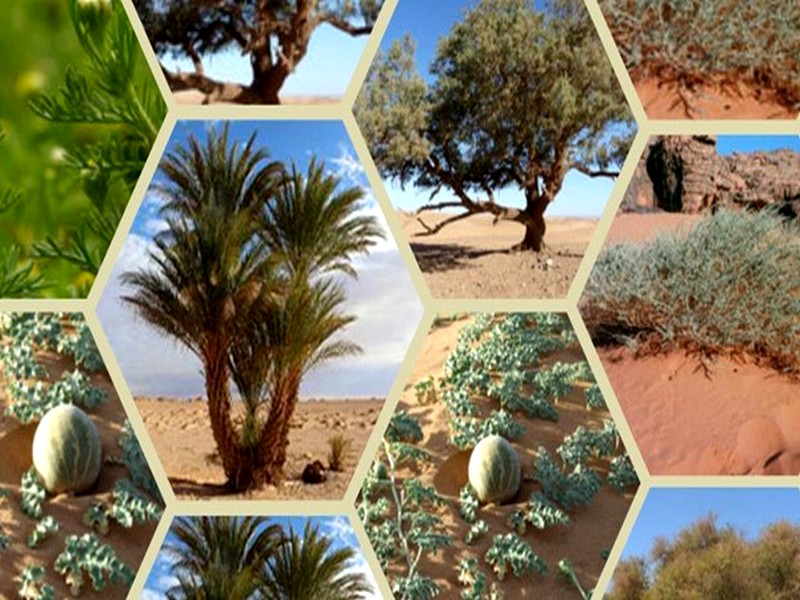
Le Géoparc Jbel Bani : Un sanctuaire de vie au cœur du désert marocain
Le Géoparc Jbel Bani : Un sanctuaire de vie au cœur du désert marocain Le désert marocain, souvent perçu comme un paysage aride et stérile, abrite en réalité une flore éto
Savoir plus...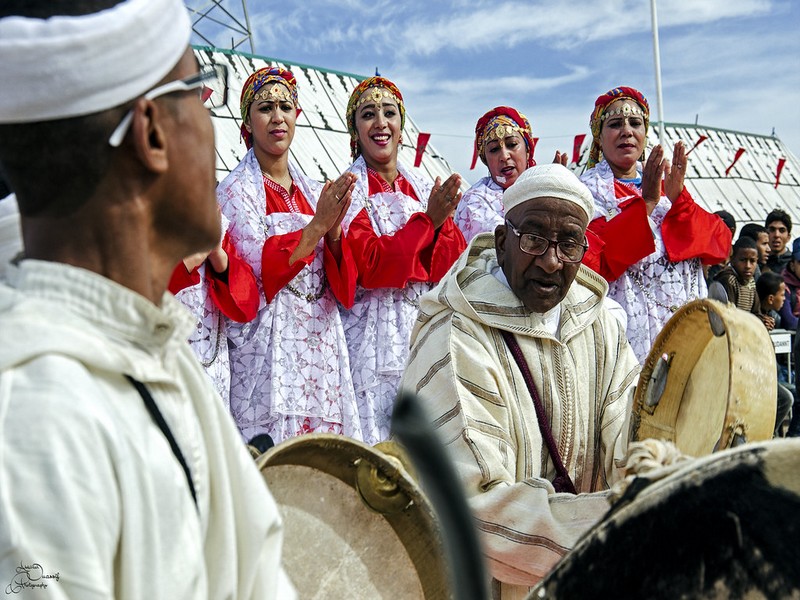
La danse Ahwach (Géoparc Jbel Bani)
La danse Ahwach (Géoparc Jbel Bani) L'Ahwach (ou ahwash) est une danse berbère répandue dans le Haut-Atlas et l'Anti-Atlas. Pratiquée durant les célébrations, cette danse varié
Savoir plus...
Préhistoire et Protohistoire du Rif Oriental
Préhistoire et Protohistoire du Rif Oriental 1. Intérêt scientifique : Le projet découle de la réflexion de mener une recherche fondamentale concernant la zone du Maghreb méditerran&
Savoir plus...
Vannerie (Géoparc Jbel Bani)
Vannerie (Géoparc Jbel Bani) Les artisans utilisent les feuilles de palmier, Doum, ou le gros jonc qui pousse dans plusieurs zones humides du Royaume, tel est le cas de l’Anti-Atlas ou dans la région de Mass
Savoir plus...
Les trois espèces de renards marocains
Au Maroc existe encore trois types de renards: le renard roux, le fennec et le renard famélique (de ruppell). Le renard roux (Vulpes vulpes) est une espèce cosmopolite, qui se rencontre dans l’ensemble du Pa
Savoir plus...
En marge de la COP22: Regards sur les réfugiés climatiques
En marge de la COP22: Regards sur les réfugiés climatiques Les associations œuvrant dans la migration foisonnent. Certaines structures sont susceptibles d’allier la cause migratoire à celle climatique
Savoir plus...
Géoparc Jbel Bani Un Levier pour un Développement Durable, Inclusif, et Scientifiquement Valorisé
Géoparc Jbel Bani Un Levier pour un Développement Durable, Inclusif, et Scientifiquement Valorisé Au cœur du Sud Marocain, le Géoparc Jbel Bani émerge comme une initiative dynamique ancr&ea
Savoir plus...Les tags en relation
En savoir plus sur " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB "
Consulter les vidéos de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les photos de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les publications de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les éditions de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les communications de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB "Recherche du site
Recherche avancée / Spécifique
Géoparc et Recherche Scientifique
Le coins de l’étudiant



Blog Géoparc Jbel Bani
Dictionnaire scientifique
Plus de 123.000 mots scientifiques
Les publications
Géo parc Jbel Bani

Circuits & excursions touristiques
cartothéques


Photothéques
Publications & éditions