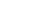A plate tectonic evolution of the Anti-Atlas on a global scale
DR.Hervé Rezeau, DR.Cyril Chelle-Michou & DR.Michael Calder
SEG Student Chapter of Geneva (Switzerland)
SEG Student Chapter of Montpellier (France)
In the western Maghreb, the Variscan (Hercynian) belt extends into the Meseta and Atlas do- mains, being widely exposed in the large Paleozoic massifs of the Moroccan Western Meseta and West- ern High Atlas, whereas it forms smaller massifs in the Eastern Meseta, Middle Atlas and Central- Eastern High Atlas (Fig.1). Altogether, these massifs define the Meseta Domain, whose late Paleozoic evolution was accompanied by significant metamorphism and magmatic intrusions. This domain is also referred to as the Meseta Block (although it was not a single block until the end of the Variscan Orogeny) and corresponds to the southwesternmost segment of the Variscan belt of Europe. The Anti-Atlas belt extends south of the Meseta Domain and can be regarded as the common foreland fold belt of both the Mesetan Variscides and northernmost Mauritanides. The Anti-Atlas belt connects to the east with the coeval, intracontinental Ougarta belt that extends essentially into the Algerian territory (Fig.1).
Figure 1: Landsat image of Morocco (from Michard et al. 2008)
The tectonic evolution of the Anti-Atlas basin and fold belt in relation to plate tectonics on aglobal scale is illustrated in Fig. 2, and summarized below (Burkhard et al., 2006):
(1)During the Panafrican orogeny, a series of terranes are accreted to the West African craton on its northern and probably western side. While the northeastern suture (Bou Azzer) and terranes to the northeast will remain in place, northwestern and western borders are subsequently reactivated and a series of terranes or continental fragments will be ripped off again during the Palaeozoic. The southwestern Anti-Atlas, however, at the margin of the Saharan metacraton remains attached to Gondwana throughout its Palaeozoic history.
(2)In Late Proterozoic–Early Cambrian, the Anti-Atlas area is in extension with the formation of many widely distributed graben and halfgraben structures, filled in with coarse clasts mostly of igneous origin. The youngest volcanism is tholeiitic–alkaline and indicates an intracontinental setting. The geodynamic significance of this extensional event is not entirely clear, however. It could be related to a southeast dipping, major and longlived subduction zone on the northwestern margin of Gondwana, causing a wide area of extension cratonward in a basin and range style.
(3)From Middle Cambrian through Middle Carboniferous, the western Anti-Atlas basin is characterized by a strong and essentially linear subsidence trend, leading to the accumulation of more than 10 km of mostly fine-grained clastic sediments, shed into an epicontinental sea from the African craton. There is little evidence in this stratigraphic record for tectonic events postulated to have taken place along the active northwestern plate margin of Gondwana. The departure of Avalon, Armorica and Hunic terranes from this margin in successive events of back-arc spreading must have brought the Anti-Atlas Sea increasingly closer to the open ocean(s) (Rheic and Palaeo-Tethys). From Silurian times onward, the Anti-Atlas Basin could thus represent the passive margin of the Palaeo-Tethys ocean, but very little if any sediments of the more distal parts of this passive margin are preserved anywhere (with the possible exception of terrains west of Guelmin and near Tineghir).
(4)In Late Carboniferous–Permian (?) compression leads to an event of strong inversion and folding. Basement is uplifted and folded into huge antiformal culminations (boutonnières) which punctuate the southwestern Anti-Atlas fold belt. The structural relief of the basement culminations is in excess of 10 km; minimum estimates of total shortening are 15 to 25 km. The Anti-Atlas belt does not represent a classical frontal, thin-skinned foreland fold-and-thrust-belt of the Appalachian–Variscan orogen, however, but rather an intracratonic, thick-skinned basement inversion belt. Similar time-equivalent belts occur further east into the African craton (Ougarta, Ahnet), but no such structures are known on the American side of the Appalachian chain.
Figure. 2: Evolution of the Variscan segments of Morocco during the Paleozoic, after Burkhard et al. (2006), based on the paleogeographic maps of Stampfli & Borel (2002). The figure is modified according to G. Stampfli, personal comm., in litt. 2008. The Meseta block is considered as separated from Gondwana (Anti-Atlas) by a Devonian Ocean (“Paleo-Tethys”). Aval, Av: Avalonian terranes; Meg: Meguma; WA/NAC: West African/North American Craton. From Michard et al. (2008).
Source web: DR.Hervé Rezeau, DR.Cyril Chelle-Michou & DR.Michael Calder unige.ch
Les articles en relation

Le gecko casqué
Le gecko casqué Le gecko casqué (Tarentola chazaliae) est un lézard de petite taille qui ne dépasse pas 10 cm de longueur. Il doit son nom à la forme de sa tête qui rappelle celle d’un c
Savoir plus...
Changement climatique : les fermes éoliennes contribuent-elles vraiment à réchauffer la planète ?
Changement climatique : les fermes éoliennes contribuent-elles vraiment à réchauffer la planète ? Depuis quelques jours, une étude menée par des chercheurs de Harvard (États-Unis) fait
Savoir plus...
MASSIF DU SIROUA
MASSIF DU SIROUA H. ADMOU1 & A. SOULAIMANI1 Structure géologique Le Massif du Siroua a été visité au début du XXème siècle par L. Gentil (1905). Il se situe dans la zone cen
Savoir plus...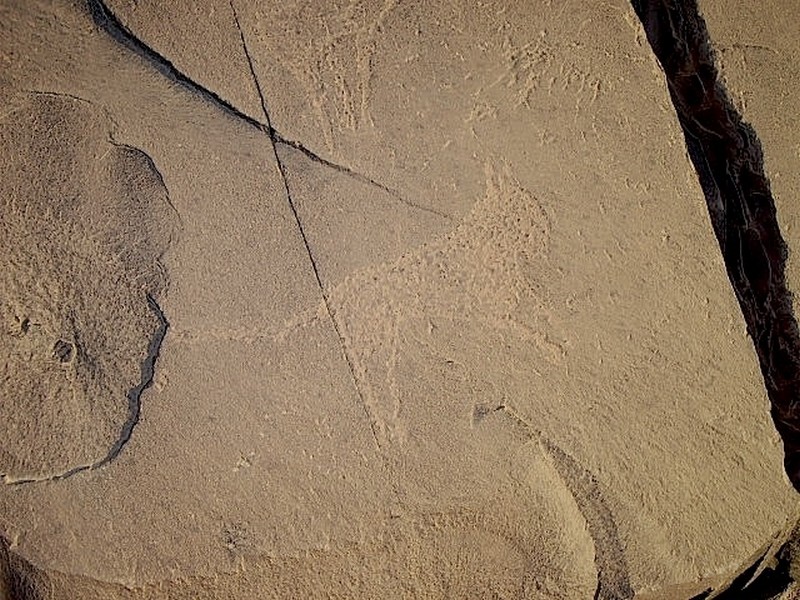
Oued Akka
L’Adrar Metgourine A 11 km au Nord d’Akka, la gara de Metgourine se présente comme un îlot dominant la plaine à un coude de l'oued Akka. Du côté Ouest, elle offre un escalier de da
Savoir plus...
Guelmim La danse de la guedra
Guelmim est considérée comme la porte du Sahara au Maroc. La ville était autrefois un centre caravanier sur la route de Tombouctou. Aujourd’hui, c’est un lieu important de commerce et d’écha
Savoir plus...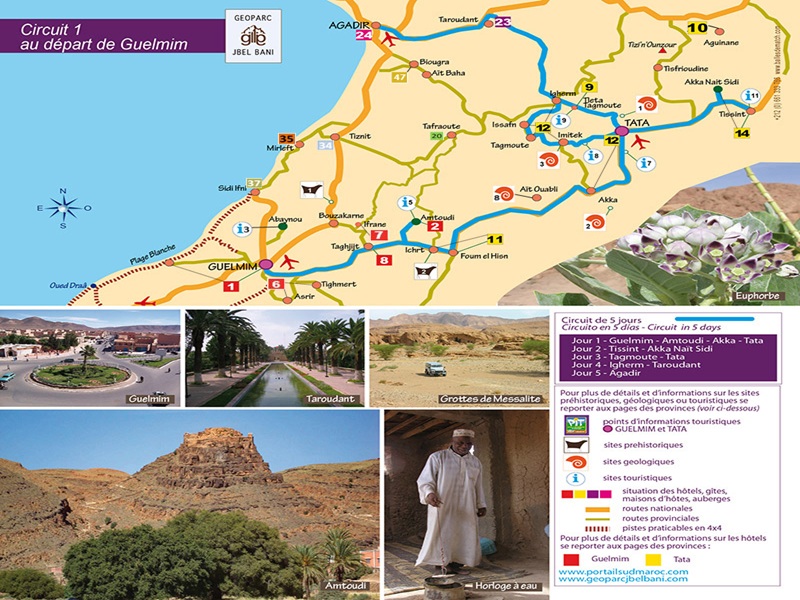
Circuit 5 jours de Guelmim vers Agadir-géoparc jbel bani
Circuit 5 jours de Guelmim vers Agadir-géoparc jbel bani Çircuit de 5 jours : Circuito en 5 dias - Circuit in 5 days Jour 1 - Guelmim - Amtoudi - Akka - Tata Jour 2 - Tissint - Akka Naït Sidi Jour
Savoir plus...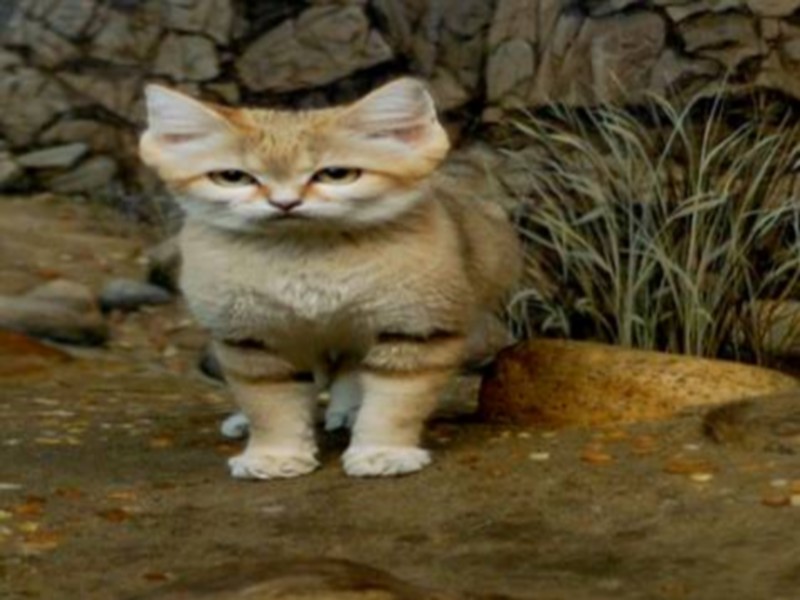
Le chat des sables
”Felis margarita”, le chat du désert Totalement adapté à la vie dans le désert du Sahara marocain, ce mammifère, dont l’existence est jugée en danger par l’UICN, reste
Savoir plus...
Utilisation de « Daghmous »
Utilisation de « Daghmous » L’alerte du CAPM Le CAPM tire la sonnette d’alarme vis-à-vis de l’augmentation de l'utilisation du « Daghmous » au vu des risques que cela peut enge
Savoir plus...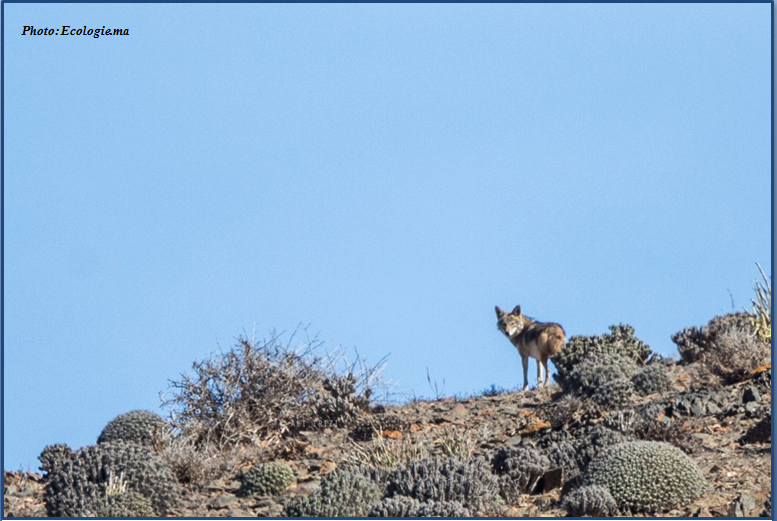
Photos: Trois jeunes canis dans l’Anti Atlas
Photos: Trois jeunes canis dans l’Anti Atlas Ali Irizi a encore frappé. Cette fois il s’agit de trois louveteaux quelque part dans l’anti Atlas. Cette fois encore la photo ne manque pas de susciter questions et &
Savoir plus...
Khettara
Khettara Khettara est une sorte de canal souterain qui draine l'eau des nappes phréatiques par gravité jusqu'à l'oasis. l'eau circule dans des galeries souterraines horizontales afin de limite
Savoir plus...
M’khinza, une plante toxique?
M’khinza, une plante toxique? Le Centre antipoison et de pharmacovigilance du Maroc (CAPM) met en garde les citoyens contre l’utilisation de M’khinza ou ansérine vermifuge. Le centre avait émis une ale
Savoir plus...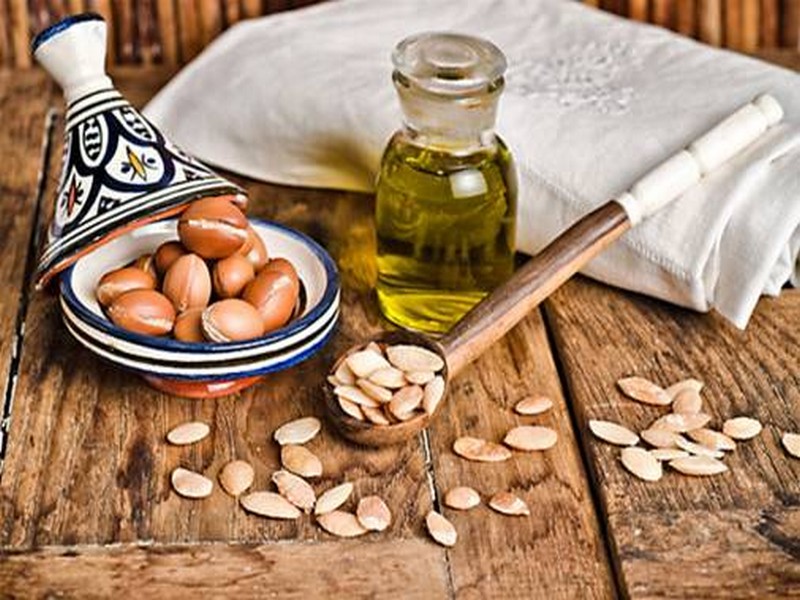
L’huile d’argan, l’élixir marocain
L’huile d’argan, l’élixir marocain Les grands chefs raffolent de l'huile d'argan, tout comme les sociétés de cosmétiques. Mais c’est uniquement au Maroc que pousse l’a
Savoir plus...Les tags en relation
En savoir plus sur " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB "
Consulter les vidéos de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les photos de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les publications de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les éditions de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les communications de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB "Recherche du site
Recherche avancée / Spécifique
Géoparc et Recherche Scientifique
Le coins de l’étudiant



Blog Géoparc Jbel Bani
Dictionnaire scientifique
Plus de 123.000 mots scientifiques
Les publications
Géo parc Jbel Bani

Circuits & excursions touristiques
cartothéques


Photothéques
Publications & éditions