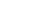
A short overview of the Anti-Atlas, Morocco
DR.Hervé Rezeau, DR.Cyril Chelle-Michou & DR.Michael Calder
SEG Student Chapter of Geneva (Switzerland)
SEG Student Chapter of Montpellier (France)
INTRODUCTION
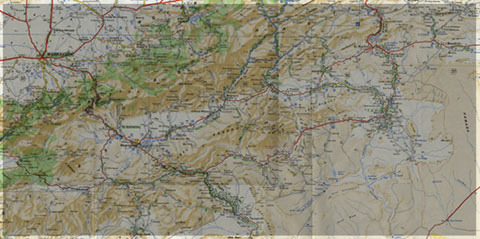
Geology of Morocco has been subdivided into four structural domains, from north to south they are the following: the Rif domain, the Meseta domain, the High Atlas, and the Anti-Atlas, as they are shown in (Figure 1).
The Rif Range extends along the Mediterranean coast from the Kabylian-Tellian belts up to the Strait of Gibraltar. South of it, the Meseta domain is located, where elevated plateaus and intramontane basins occur. Further south the High Atlas system is found, which displays several massifs close to 4000 m, including the highest peak of northern Africa (Jebel Toubkal). The Middle Atlas represents a branch of the Atlas system that extends obliquely across the Meseta domain, and exceeds 3000 m in elevation. Finally, the Anti-Atlas domain is found, which rises forming a massive mountain that achieves up to 2700 m. Further south the elevation decreases both southward and westward from ca. 1000 m to less than 200 m close to the Atlantic.
Figure 1: Elevation map of Morocco and neighbouring countries from GTOPO30 database (A. Michard et al. 2008)
GEOLOGICAL SETTING OF THE ANTI-ATLAS
The Anti-Atlas mountain belt is located in the northern part of the West African Craton (WAC). It is stretching NE-SW and is characterized by Precambrian to late Proterozoic rocks covered by younger sediments of Edicaran to Cambrian in age. The geological boundary between the Anti-Atlas and High Atlas is structurally marked by the South Atlas fault (SAF) (Fig.2). The Anti-Atlas massif is a zone of wide domal uplift with much weaker Alpine age deformation. The volcanics and conglomerates rocks from the Ouarzazate & Bou Salda group in the North-East are surrounding the older volcanics rocks
The Anti-Atlas mountain belt is located in the northern part of the West African Craton (WAC). It is stretching NE-SW and is characterized by Precambrian to late Proterozoic rocks covered by younger sediments of Edicaran to Cambrian in age. The geological boundary between the Anti-Atlas and High Atlas is structurally marked by the South Atlas fault (SAF) (Fig.2). The Anti-Atlas massif is a zone of wide domal uplift with much weaker Alpine age deformation. The volcanics and conglomerates rocks from the Ouarzazate & Bou Salda group in the North-East are surrounding the older volcanics rocks and turbidite sequences from the Sahgro Group and the Pan-African granite intrusions. This geomorphological feature is commonly called inliers (“boutonnière” in French) and is the result of an exposed older rock formation surrounded by younger rock, and is due to a high erosion rate of rocks with different hardness but also encouraged by deformation such as folding and faulting (Gasquet et al. 2005). Several slivers of ophiolites are present in the Anti-Atlas belt, the best preserved are situated in the Bou Azzer, Siroua and Iriri region, which represent remnant of an ocean closure. The basement is composed of schists, granites and mylonites of Paleoproterozoic age. The latest Variscan and Alpine orogenic events overprint most of the Anti-Atlas geological province and thus complicate the Pre- Cambrian geodynamic interpretation. However, two main periods of tectono-thermal magmatic activity (Gasquet et al. 2005) are now recognised :
(i)A Palaeoproterozoic period, corresponding to the Eburnean (Birimian) orogeny,
(ii)A Neoproterozoic period, corresponding to the Pan-African orogeny.
Figure 2: Schematic map of the Anti-Atlas Precambrian inliers (Boutonnière), and location of the maps, satellite views and lithospheric profile presented hereafter (Gasquet et al. 2008)
Source web : DR.Hervé Rezeau, DR.Cyril Chelle-Michou & DR.Michael Calder unige.ch
Les articles en relation
Paléontologie
Paléontologie La paléontologie est la discipline scientifique qui étudie les restes fossiles des êtres vivants du passé et les implications évolutives de ce
Savoir plus...
Que voit une mouche ?
Que voit une mouche ? Les yeux de mouche sont gros, ils prennent toute la place sur la tête de l'insecte et sont rouge vif. Cela veut-il dire que la mouche voit rouge et en grand format ? Pas tout à fait, mais sa vis
Savoir plus...
Le Sahara marocain
Le Sahara marocain Terre aride et inhospitalière, le Sahara marocain n’en reste pas moins d’une importance centrale dans l’histoire des civilisations au Maroc. Depuis le onzième millénaire avant
Savoir plus...
Sablo-thérapie :Zagora - l'été des bains de sable au Sud marocain
Sablo-thérapie :Zagora - l'été des bains de sable au Sud marocain Le bain de sable votre médecin naturel Zagora vous présente des étendues de sable brulant aperte de vue, c'est la ou
Savoir plus...
Comment sécuriser la ressource hydrique
Comment sécuriser la ressource hydrique Trois nouveaux axes en phase d’être déployés Priorité au dessalement et au recyclage des eaux usées La rareté de l’eau gagne p
Savoir plus...
Sommet climat à Paris: 100 pays invités mais pas Trump
Sommet climat à Paris: 100 pays invités mais pas Trump Une centaine de pays ont été invités au Sommet de Paris sur le climat du 12 décembre mais « pour l’instant » pas le pr
Savoir plus...
BIOCLIMATS et MILIEU PHYSIQUE (jbel Lkest )
BIOCLIMATS et MILIEU PHYSIQUE (jbel Lkest ) Caractéristique bioclimatique : - Inframéditeraranéen aride semi-aride tempéré au piémont - Thermoméditeranéen semi-aride. -
Savoir plus...
Restauration des Igoudars : le grenier d'Immchguiguen renaît dans l'Anti-Atlas
Restauration des Igoudars : le grenier d'Immchguiguen renaît dans l'Anti-Atlas La région de Souss-Massa poursuit ses efforts pour préserver et valoriser son patrimoine culturel unique. Dans l’arri&eg
Savoir plus...
4 planètes géantes découvertes autour d’une jeune étoile surprennent les astronomes
4 planètes géantes découvertes autour d’une jeune étoile surprennent les astronomes Quatre planètes géantes qui orbitent autour d'une étoile. Surprenant ? Oui, compte tenu de
Savoir plus...
Déserts du Maroc
Si le Maroc, dont l’échine dorsale semble être cet Atlas majestueux qui le parcourt, est un pays montagneux largement ouvert sur la mer et bordé de grandes plaines côtières, le désert tient
Savoir plus...
Circuits Fascination Anti-Atlas
Pour simple Berline : Tiznit ou Taroudant - Tafraout - Igherm - Tata - Akka - Assa - Guelmim - Agadir Avec 4x4 : Plage Blanche - Oued Draa - El Ouatia - Tan Tan - Asrir. HISTOIRE ET CULTURE On sait aujourd’hui que la pl
Savoir plus...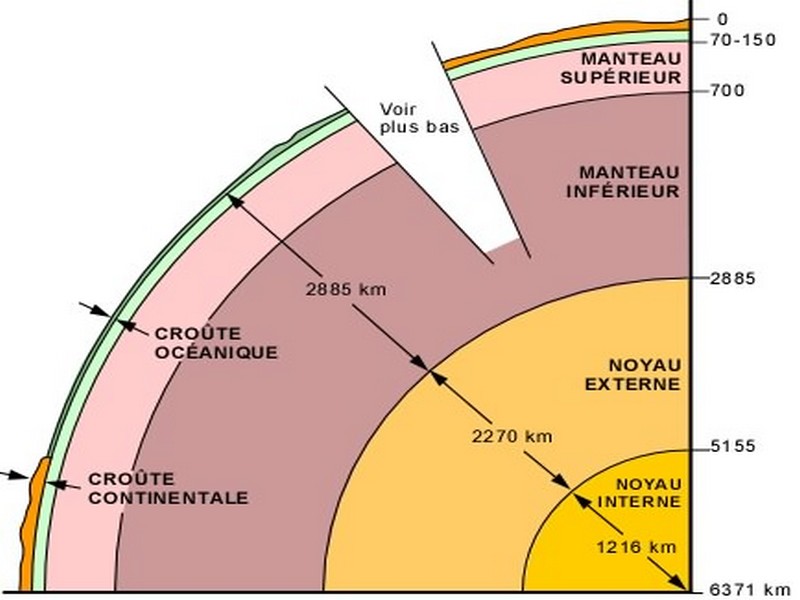
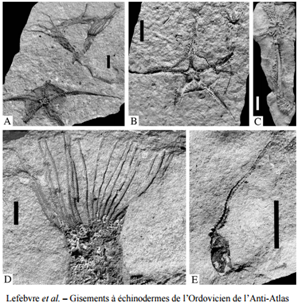
La structure interne de la Terre
L'intérieur de la Terre est constitué d'une succession de couches de propriétés physiques différentes: au centre, le noyau, qui forme 17% du volume terrestre et qui se divise en noyau interne s
Savoir plus...Les tags en relation
En savoir plus sur " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB "
Consulter les vidéos de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les photos de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les publications de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les éditions de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les communications de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB "Recherche du site
Recherche avancée / Spécifique
Géoparc et Recherche Scientifique
Le coins de l’étudiant



Blog Géoparc Jbel Bani
Dictionnaire scientifique
Plus de 123.000 mots scientifiques
Les publications
Géo parc Jbel Bani

Circuits & excursions touristiques
cartothéques


Photothéques
Publications & éditions